By Anouk, Katharina, Sabina, and Soraya
It has become nearly impossible to watch the news, open social media, or even attend a social gathering without a person mentioning “crypto” (cryptocurrency). With the emergence of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies, the financial world has fundamentally changed. This blogpost will focus on the impact of cryptocurrencies on money laundering practices, including the problems that this development has caused for law enforcement. Even for the new EU Agency AMLA, it remains to be seen whether they have the resources to effectively investigate these new cases of money laundering. Cryptocurrency uses blockchain technology, which provides for a high level of anonymity, making investigations into money laundering cases more difficult when cryptocurrency is involved. This will be explained after a brief overview of money laundering is provided
Money laundering
Money laundering has been around for over 3000 years. It started when physical money was still the only relevant form of payment, but then evolved into a large and intricate digital system. Given its impact on the financial system and its close link to organised crime, this development in money laundering is in need of proper regulation. Investigation of money laundering cases can prove to be difficult, especially when the traditional methods of investigation are no longer sufficient. These methods include undercover police informants, reports on suspicious activity by companies, and the collapse of a company leading to a lot of information to be exposed. Right now, these methods do not suffice due to the anonymous and decentralised character of blockchain, which will be explained in the next section.
How does cryptocurrency work?
Let’s circle back to cryptocurrencies. Cryptocurrencies are officially named “virtual decentralised currencies” by Europol. In this name there are three elements: virtual, decentralised, and currency. It is a payment method that only exists in the digital realm, it does not have one centre where it is managed and data is kept, and it serves as money. The decentralisation of currency is the largest change in our understanding of the financial world. Usually, transactions are tracked by a bank and there are data controllers that check whether there is suspicious conduct. When this is the case, it means that finances are centralised. Cryptocurrencies, however, use the decentralised blockchain technology. This means that the transaction data is not found in one central database controlled by, for example, a bank.
Bitcoin was one of the pioneers in blockchain technology. This technology ensures an incredibly high level of anonymity when making transactions using cryptocurrency. For this reason, it is difficult to trace transactions. There are bitcoin users that use the technology for regular purposes or as an investment, but it has also made it easier for criminals to make transactions in illicit practices. It is difficult for law enforcement agencies to trace down transactions when blockchain technology is employed. But what is blockchain and why is it so anonymous?
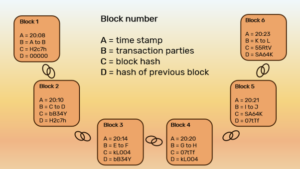
Visualization by Soraya (2024)
In the image above, you can see the way in which blockchain operates. You start with block 1, the first transaction. This block contains a small collection of data: a time stamp, the transaction information, its own hash (a sort of personal “code”) and the hash of the previous block. Of course, this is block 1 so there is no previous block. In block 2, you see the same forms of data, including the hash of block 1 under D. As can be deferred from this, you can find a previous block via its hash, but you can’t go forward. The transactions are out in public, but the information of the person behind the transaction can only be found by the person that has the “private key” to the transaction. You can see this private key as a secret password that is needed to unlock the personal information behind the transaction, such as a passcode.
What does this mean for the authorities?
Now that the technology has been illustrated, its implications for law enforcement must be explained. Blockchain counts for a high level of anonymity. In a society where data is collected everywhere and all the time, there is a large demand for platforms where people feel a little less “watched”. However, it is also noteworthy that this anonymity can harm criminal investigations into money laundering to a large extent. Moreover, tackling this challenge is like trying to solve a gigantic puzzle, especially when you consider that one chain can involve thousands of transactions.
A proposal for the establishment of an authority that concerns itself with money laundering (AMLA) has been brought to life by the EU (European Union). One of its goals is to improve the enforcement system regarding money laundering, since it was not one comprehensive system before. If the providers of cryptocurrency services are established as entities that fall under the scope of AMLA’s direct enforcement powers, AMLA would be competent to investigate these entities. However, it is still unknown how AMLA will attempt to do this.
This video gives a short explanation of why AMLA is introduced.
Source: EU Finance: AMLA – the new EU Anti-money laundering Authority
What can AMLA do about this issue?
Sufficient investigation into money laundering where cryptocurrency is involved requires blockchain technology to be used by the investigation team in combination with AI tools. However, the AMLA proposal does not explicitly address whether AMLA possesses the resources for employing such innovative tools. It is also not known whether AMLA is allowed to employ AI to investigate the books of the cryptocurrency provider. In recital 6 of the proposal, it is stated that AMLA must combine ‘independence and a high level of technical expertise’. However, there is no mentioning of this technical expertise when the investigative powers of AMLA are discussed further on in the proposal.
It is not known how AMLA is planning to tackle these issues, since it is merely in its draft phase. However, it is important that AMLA considers the inclusion of investigative powers regarding cryptocurrencies explicitly, since it is unclear whether sufficient measures are taken to combat the issue of money laundering using cryptocurrency. Resources regarding computing power and expertise must be created for AMLA to effectively investigate this issue. The effectiveness of AMLA remains to be seen, but its creation is a step towards a more sufficiently regulated and secure cryptocurrency landscape.
- [DRAFT] Frontex’s duties and refugees’ rights: an effectiveness vs. legality example at the EU borders. - April 11, 2024
- [DRAFT]EPPO in its first test before the CJEU: Case C-281/22 G.K. and Others (Parquet Européen) - April 11, 2024
- The Fundamental Rights Officer: Just what the EUAA needed - April 11, 2024
